An advanced phishing schedule, consisting of a network of fake websites, has been focusing on Web3 projects for years and is the draining of cryptocurrency portfolios on a scale.
First detected by Validin as a simple network of crypto phishing websites in April 2024, it soon became clear that the schedule can be much more advanced and large -scale. This led to the provider of Internet Intelligence Platform cooperating with the Sentinelone research team, Sentinellabs, to conduct further research.
Instead of trusting common delivery methods such as phishing e-mails, SMS (SMIish), social media messages and blog comment spam, the schedule, freedrain called by the researchers, used SEO manipulation, free web services and layered diversion techniques to focus on cryptocurrency portfeiles.
The operation, probably performed by a team based in India (or possibly Sri Lanka), has been going on since at least 2022.
Validin and Sentinellabs published their findings at Pivotcon 2025, a conference conference of threats in Malaga from 7 to 9 May.
Discover a large-scale crypto phishing network
In April 2024, Validin published a report with a series of crypto-draining phishing pages.
This report caught the attention of a person who contacted Validement, and claimed that he lost 8 bitcoins, worth around $ 500,000 at that time.
“The victim had unconsciously submitted their wallet seed to a phishing site while trying to check their wallet, after he had clicked on a highly ranked search engine result,” explained the Sentinellabs and Validin researchers in a joint 8 May report.
A seed sentence, also known as a recovery sense or mnemonic seed, is a list of words used to restore a cryptocurrency wallet and gain access to the corresponding funds.
It was confirmed by trusted cryptocurrency tracking analysts that the zoning portion of it used to receive the funds from the victim was a one-time use.
They stated that the stolen assets were quickly moved by a cryptocurrency mixer, an obfuscation method that fragments and launders funds over multiple transactions fragments, which made attributing and recovery almost impossible.
The researchers reported that although they were unable to help recover the lost assets, the outreach effort has shown that the phishing attack was part of a broader, large-scale operation.
SEO manipulation techniques
Upon further investigation, the Sentinellabs and Validusin researchers identified 38,048 different Freedrain subdomains that host art pages. These subdomains are hosted on cloud infrastructure, such as Amazon S3 and Microsoft Azure Web Apps, which simulate legitimate cryptocurrency portion in interfaces.
To make the network of phishing websites more attractive for victims, hackers used a combination of SEO manipulation techniques, free web hosting services (eg github.io, WordPress.com, Godaddysites, Gitbook), typosquate techniques, known visual elements and layered redirection techniques.
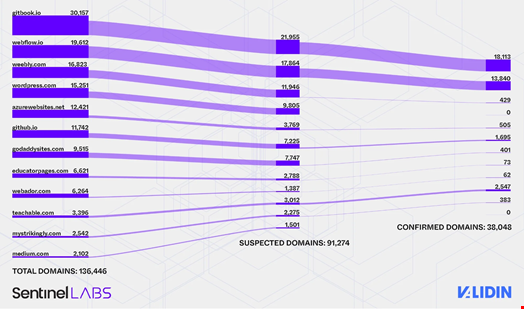
“We were amazed by the enormous amount of bait pages that appeared under the best -ranked search results in all major search engines,” the researchers said.
“In most cases, the pages consisted of just a single large image (again, usually a screenshot of a legitimate crypto wallet -interface) followed by a few lines of text that seemingly useful instructions offered, ironically, some even claimed to inform users about how they could avoid phishing.”
Although apparently simple, these web pages have direct answers to questions that search engine users will probably type. These types of pages are known to be rewarded by algorithms for search engine, especially when they are hosted on platforms with a high reputation.
In addition, the Freedrain operators used large-scale commentary Spamt on poorly maintained websites to increase the visibility of their artificial bait pages through search engine indexation-a technology that is known as spamdexing.
“With this technique, Freedrain can bypass traditional delivery vectors such as phishing -e -mails or malignant advertisements, instead to meet victims exactly where they look at the top of trusted search engines,” the researchers wrote.
AI-Aided Content Generation
The text on many artificial pages showed the evidence that, according to the researchers, they were generated by large language models.
They stated that artifacts were found for copypasta, where the specific used tools were unveiled, including curves such as ‘4O Mini’, probably a reference to the GPT-4O-mini model from OpenAi.
The researchers noted that these signs suggested that the Freedrain operators used generative AI to create scalable content, but sometimes did this carelessly.
The attack chain: a step -by -step split
The researchers of Sentinellabs and Validation were able to outline the step-by-step process that ultimately leads to the phishing site:
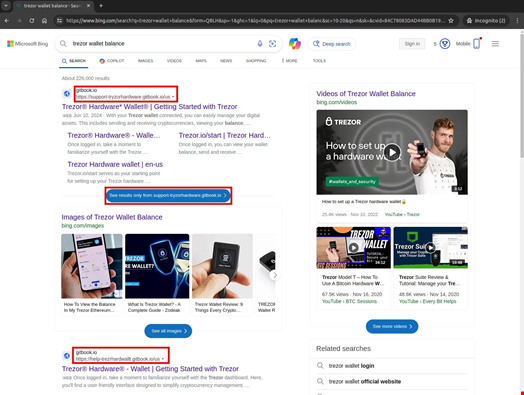
- Search for wallet-related questions (eg “Trezor Wallet Balance”) on a large search engine
- Click on a high -ranking result, often hosted on an apparently reliable platform such as Gitbook.io or WebFlow.io
- Country on a page with a large, clickable image (usually a static screenshot of the legitimate wallet interface)
- Click on the image, which either leads to a phishing page whether the user is diverted to an intermediary site
- Come on the latest phishing site, an almost perfect clone of the real wallet service, so that the user enters his seed sentence
Once a seed sentence has been submitted, the automated infrastructure of the attacker will tap money within a few minutes.
Attribute the Freedrain campaign
Finally, the researchers stated that attributing the Freedrain operation was a challenge because of the short-lived infrastructure and the use of shared, free services.
However, by analyzing metadata, behavioral signals and timing artifacts, they were able to collect significant insights into the characteristics of the operators, including their likely location, work patterns and coordination level.
The researchers reported that their investigation revealed various important findings. They analyzed Github repositories associated with Freedrain and discovered that the E -mail addresses used in the commits were unique and were linked to individual Github accounts, with most of free E -mail providers.
In addition, the Commit time stamps were mainly in the UTC+05: 30 -time zone, corresponding to Indian Standard Time (IST), which suggests a strong geographical link to India -or possibly Sri Lanka.
This finding was confirmed by analyzing metadata from other services, such as WebFlow, which unveiled a clear work pattern of 9 to 5 weekday in the IST-Tijdzone.
The researchers concluded that, on the basis of the combined evidence, it was very likely that the Freedrain operation was carried out by persons based in India and became work on weekdays.
They also noted that the campaign was active since at least 2022, with a significant increase in the activity in mid -2024 and remained active at the time of their report.
Mitigation recommendations
The researchers recommend that platforms take free tier steps to prevent abuse and to improve their reaction to malignant activities, as emphasized by the Freedrain campaign:
- Improving mechanisms for reporting abuse by allowing abuse to be reported directly from published content pages and direct lines of communication with trusted threats Intel analysts and threat researchers
- Invest in basic abuse prevention -tooling to check for patterns of abuse, such as making bulk areas, similar domain instructures and repeated hosting of external phishing -kits
- Improving detection possibilities to identify coordinated abuse, such as repetitive naming patterns and identical templates reused over subdomains



